The first "vaccine" for bees is licensed in the United States - Nexus
Currently used by a limited number of beekeepers for two years, this product is presented by the laboratory that designed it and by the media as a great solution. No questions about the tests that validated it or its possible effects on the long term.
◆ Few current remedies
Explain the researchers of the Dalan Animal Health-funded study” American foulbrood disease (AFB) is a highly contagious bacterial brood disease that affects honey bees (Apis) and causes hive losses worldwide.
The etiological agent is the Gram+ Paenibacillus larvae bacterium, which is capable of infecting bee larvae during the first 3 days of life. It can be found in hives around the world with viable spores for decades. Antibiotics [interdits en Europe pour les abeilles] they are largely ineffective in treating disease as they are only effective against the vegetative state. […] The spores can persist for decades in the environment, remaining virulent throughout this period, and therefore pose a permanent threat to honey bee colonies. »
◆ Far from traditional vaccines?
If we have put the words “vaccine” and “vaccinating” in quotation marks in the title and in the introduction of this article, it is because in reality, as explained in an article published on the CARI website in Belgium, the bee, if in fact has a innate immune system that allows him to defend himself against pathogens, cannot really be vaccinated as we hear in vertebrate animals and in humans: ” Like other insects, it cannot permanently acquire the antibodies that will protect it from this or that disease: it has no acquired immunity. Clearly it’s impossible to vaccinate her, her body can’t keep track of the resistances she may have built up to counter the intrusion of pathogens. »
It is therefore not by injecting or vaporizing a product containing a low level of attenuated or inactivated bacteria that bees will be able to be immunised.
It is through the transmission of transgenerational immunity that protection occurs. The process involves introducing product containing the larvae that have succumbed to American foulbrood to royal jelly, which the worker bees give to the queen.
◆ A series of tests carried out on non-wild bees
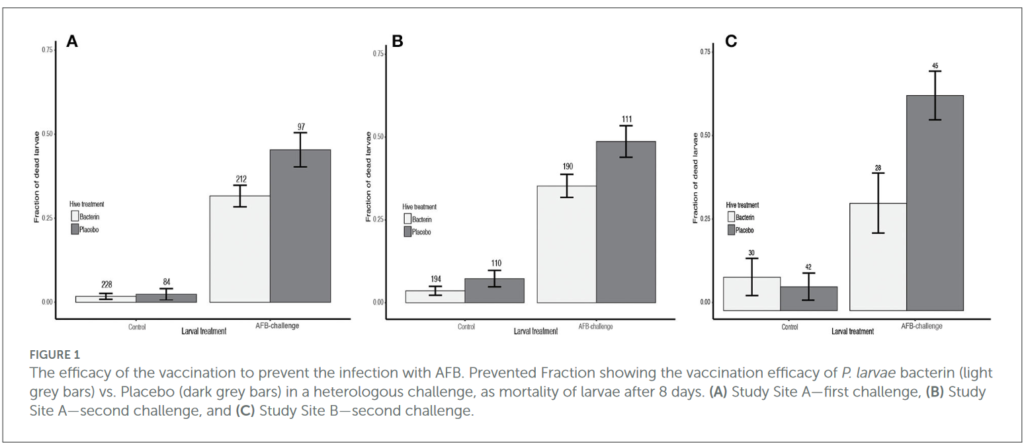
Two separate tests were performed at two different sites. Study site A was located in Graz, Austria, with 20 colonies vaccinated against AFB bacteria and 10 placebo hives. Study center B was in Marchamalo in Spain, with 15 colonies vaccinated against AFB bacteria and 15 placebo hives. The subspecies of honey bees Apis mellifera carnica was used in Austria and Apis mellifera iberiensis in Spain. In both cases, only hives with enough larvae (30 per hive) were included in the study (the others were excluded because the queen had not produced any larvae).
The conclusion of the study that allowed the still restricted authorization of the vaccine is that ” AFB infection can be reduced by approximately 30-50% under laboratory conditions after vaccination of female queens “.
As the study also states that when a hive is contaminated, ” the only effective way to eradicate it and prevent the spread of the disease is to burn the hive, the equipment and the colony », one can already ask whether a reduction in the contamination of the number of bees inside a hive will prevent the destruction of this hive…

The study does however specify that several hives experienced queen failure and that hive losses were ” a bit high (about 30%) “. Having said that, it would not have been found” no difference in hive losses between colonies treated with placebo and those treated with bacteria “.
He also points out that ” due to the highly contagious nature of AFB, hives cannot be tested for in the wild. Bees (which are wild animals) also cannot be kept in captivity, as a single hive contains between 10,000 and 30,000 (up to 80,000 in some cases) individual bees, which would have to fly out and forage within a 10 km radius . »
We can therefore ask where and how the “full-size test” currently conducted among several beekeepers in the United States over a two-year period and quoted by France TV is taking place…
◆ A brief summary of the studies
If it was known before 2015 that some pathogens could be transmitted from a female insect to her offspring, it was a study published that year by scientist Dalial Freitak and his colleagues that allowed to increase certain knowledge. The study concludes that an essential egg yolk protein, vitellogenin, mediates the transport of transgenerational immunity in insects.
In 2019, Freitak and other researchers reported on the interaction between worker bees and the queen through the sharing of vitellogenin through royal jelly. Then, in 2021, Freitak et al determined that when a bacterium is ingested by a worker bee, the pathogenic fragments are incorporated directly into royal jelly.
It is from these results that, funded by Dalan Animal Health, Dalial Freitak together with other scientists developed Paenibacillus Larvae Bacterin, the “vaccine” against the American foulbrood. In their 2022 study, they claim to demonstrate “ an increase in the survival of infected honey bee larvae after their queen has been vaccinated, compared to the offspring of placebo-vaccinated control queens “.
How does the product work? Dalan Animal Health explains: “ Worker bees consume the vaccine mixed with soft, mushy sugar, which is then digested and transferred to the glands that produce royal jelly for the queen. […] She ingests it and fragments of the vaccine lodge in her ovaries. Having been exposed to the vaccine, the developing larvae are immune when they hatch. In other words, when the vaccine is consumed by a queen through royal jelly, it can be transmitted directly to her larvae.
In summary, the “vaccine” allows the innate immunity of the bee to be modified by generational transmission.

◆ Questions not mentioned
Even if, according to France TV, this vaccine is not genetically modified and can be used in organic farming, and even if we speak for example in The echoes of a “protective serum”, it would also be good to ask a few questions to find out if the product presented is really as beneficial as one seems to believe from the outset, based solely on the press release from the manufacturing laboratory.
One might wonder whether it is acceptable that the founders of the study sponsor, including Dalial Freitak, are themselves the authors of the study and the makers of the “vaccine” product, as clearly stated in the “conflict of interest” section.
Consider whether independent “guardians” existed to monitor the study, whether and how bees will be monitored on a large scale, and how long-term side effects will be determined. Whether surrounding unvaccinated bees can be affected and how. What was expected if the product was found to be harmful to the bees tested and to bees located not far from the tested locations.
Ask yourself what could be done to prevent diseases as much as possible by preserving nature, rather than modifying its internal functioning, up to the immunity of bees. And the impact this addition to royal jelly might have on humans when they ingest honey…
Our Director of Publication was invited to speak on this topic and more generally on vaccines on January 18, 2023 in the program Straight broadcast on Radio Courtoisie. He referred to these kinds of questions to ask and emphasized that “ for our leaders, the vaccine has become the only way to cure people! »
👉 Watch the full show on YouTube:
In an ideal world, the proven, perceived or possible weaknesses of a product sold would be exposed as much as its strengths by its creator, but if we also rely on the management of the Covid crisis, we can be sure that this is not currently the case and that without becoming paranoid, we must remain vigilant. Especially with regard to bees, pollinating insects essential for our survival as a whole.
We will therefore pose some questions raised in this article to Mr. Freitak, one of the lead authors of the study, a study of which we did not understand all the points. We will come back to you if we have answers…
Article by Estelle Brattesani
Picture of Matthew Greger of Pixabay
👉 Read our file on the composition of vaccines in our number 144 (January-February 2023):

👉 Read our dossier on bees in our number 124 (September-October 2019):

TO SUPPORT OUR MAGAZINE
✰ 112 pages, 100% INDEPENDENT and AD-FREE! ✰

Nexus OFFER 🎁
SUBSCRIBE ✨
👉 DEAR READER, WE NEED YOU! In addition to its print magazine, Nexus offers you 100% FREE web content.and information 100% FREE! We remind you that Nexus does not benefit from any public or private subsidy and lives thanks to its readers, subscribers or donors.
To support us you can:
✅ Subscribe to Carta & Digitale magazine
✅ Nexus offer
✅ Browse all our numbers and order them individually
✅ Make a one-time or regular donation to TIPEEE or PAYPAL
✅ Check out our latest issue on newsstands or online

![]() Let’s keep in touch, find us on other social networks
Let’s keep in touch, find us on other social networks![]() Sign up to our newsletter
Sign up to our newsletter


Commentaires
Enregistrer un commentaire